Text rendering quality is an amazingly complicated topic, with hardware, settings, fonts, differing rendering engine philosophies, and user preferences all playing key roles. In some cases, however, almost everyone can agree that one rendering is superior to another. Consider, for instance, the text of this Gizmodo article as seen on one user’s computer:
Oct 04, 2016 Microsoft Edge and Remote Desktop (Both UWP Apps) don't start When I try opening either of the apps on my laptop, they just show the splash screen, then close. I've tried quite a few of the suggestions from other posts, but they're a year old and none of the solutions worked. Form filler that obtains entries from Remote Desktop Manager and Devolutions Password Server Devolutions Web Login is a free browser plugin used in conjunction with Remote Desktop Manager, Devolutions Password Server and Devolutions Password Hub which allows users to securely and automatically inject passwords into websites using credentials stored in their vaults.
You can use this fancy swipe-view widget to wipe between the renderings of the full paragraph:
Most people think the text for Edge looks awful, with unexpectedly chunky letters and irregular kerning, but the text for IE11 looks pretty good.
Investigation reveals that the problem here is that Edge and Firefox are respecting the system’s font smoothing setting, but IE11 is ignoring it.
Font Smoothing in Windows
Windows has three levels of font smoothing: Off, Basic/Standard, and ClearType. Here’s a quick chart showing the impact of each setting across three browser engines:

Notably, the IE11 rendering is pixel-for-pixel identical regardless of Windows settings– it renders with grayscale subpixel smoothing even when smoothing is off or ClearType is enabled. In contrast, if you zoom into the ClearType examples in Edge 86 and Firefox 80 you can see subpixel smoothing at work, with tiny colored fringes smoothing the edges of the characters.
Examining Smoothing Parameters

Font Smoothing is controlled by four registry values inside HKCUControl PanelDesktop. FontSmoothing supports two values {0=Off,2=On} and FontSmoothingType supports values {1=Basic,2=ClearType}. The FontSmoothingGamma parameter controls the darkness of the smoothing and accepts values between 1000 and 2200. You have to zoom in pretty close to see the effect:
The FontSmoothingOrientation flag controls the order of the red, blue, and green pixels in the display; it supports two values {0=BGR, 1=RGB}; ClearType needs this information to understand which subpixels to illuminate when smoothing. RGB is the most common and the default.
Applications that need this information should use the SystemParametersInfo function to retrieve these parameters.
Remote Desktop For Edge Browser
Tuning Parameters
End-users can enable FontSmoothing in the Windows Performance Options (Win+R, then SystemPropertiesPerformance.exe):
Remote Desktop Connection
To enable ClearType and tune its settings for your displays and settings, run the ClearType Tuner Wizard (Win+R, then CTTune.exe):
The Tuner will walk you through a series of side-by-side text renderings, asking which of them looks best, a bit like an eye doctor determining the parameters for your prescription eyeglasses.
Note: If you use a Windows PC via a remote desktop connection, ensure that the “Font Smoothing” option is checked in the connection properties:
…and that font smoothing wasn’t disabled via policy on the remote server.
Checking Edge Status
You can determine what font smoothing method is presently used in Edge by visiting the URL edge://histograms/Microsoft.Fonts.FontSmoothingMethod
The histogram will show a datapoint for the current state, where
0= No Smoothing1= Grayscale (aka SUBPIXEL_RENDERING_NONE)2= ClearType
Other Culprits?
Windows settings do not account for all cases of text rendering dissatisfaction.
In some cases, the problem is that a website has selected a font not present on the user’s PC, forcing fallback to an inferior font lacking proper hinting data for smoothing. Within Chromium itself, the browser changes the default fixed width font from Courier New to Consolas if ClearType is enabled, because the latter has better hinting information. Similarly, in Edge 85, we improved font fallback for Chinese to prefer the (ClearType-optimized) Microsoft YaHei and Microsoft JhengHei fonts over legacy fonts.
In other cases, users may simply prefer darker text than ClearType generates, perhaps using a browser extension to achieve their preferences.
In other cases, the user’s hardware might not be optimally configured for font smoothing. For instance, if you run a monitor in Portrait mode, its pixels have a different layout. A device can report its subpixel geometry using a registry key.
If you see a case of poor text rendering across browsers that you cannot explain using the information in this post, please let us know about it!
-Eric
We have a new internet browser! Microsoft Edge based on Chromium, available and supported on Windows 7, 8 and 10 and most importantly in Windows Server 2008 R2, 2012/2012 R2, 2016 and 2019. This means that we now have a modern and secure browser that can be managed via Group Policy and is supported by Microsoft in a server operating system.
I have been using this browser for quite some time now and it is awesome. One of the really great features is that you are able to install browser extensions from the Google Chrome Web Store, as Google Chrome has been available for a very long time, there are a lot of available extensions.
However with that said Microsoft now finds themselves in a situation where they offer a browser based on Chromium, which is an open-source project, which then again means that Microsoft does not control the entire code in the Edge browser. I am really excited about how Microsoft will handle this in the future.
Get the Edge Installer
So, how do we get the browser up and running in a Citrix VDA? We’ll start with downloading the enterprise MSI file here:
Edge administrative templates
And while there, we’ll also grab the administrative templates which enables us to configure around 200 different settings in the browser. Remember to copy the administrative templates to your Central Store.
Edge security baseline GPO
Microsoft has also created a security baseline GPO which can be found here:
With this, we are now ready to install and configure the new Microsoft Edge browser.
Installing the Microsoft Edge browser
Before installing the browser, be aware that you will have to prevent the Citrix API hooks from latching themselves onto the Microsoft Edge process. Citrix has an article on how to disable Citrix API hooks on a per-application basis. Two options are described in the article, I am using the option for XenApp and XenDesktop 7.9 or later. So your UviProcessExcludes value name should look like this:
What you need to do is to add the msedge.exe to any existing value data. This change requires a reboot, so you will have to apply this when installing the browser.
I have created a small PowerShell script which will add the msedge.exe value to any existing value data:
The Microsoft Edge browser also creates a shortcut on the public desktop (C:UsersPublicDesktop). I always recommend deleting application shortcuts on the public desktop, as I prefer to control which application shortcuts appear on the user’s desktop. Unfortunately deleting the shortcut on the public desktop is not enough, a shortcut is also created on the user’s desktop (C:Users%username%Desktop) during first logon, even though we deleted the shortcut on the public desktop.
This behavior is not new to me, it is also seen with the Google Chrome browser .
To prevent the shortcut from being created on the user’s desktop, a “master_preferences” file has to be copied to the C:Program Files (x86)MicrosoftEdgeApplication folder, overwriting any existing master_preferences file.
UPDATE – 21-04-2020 (April 21st 2020): As of v81.x stable build it is now possible to use an install parameter, to prevent the creation of a desktop shortcutduring user logon, a desktop shortcut is still created in the Public user desktop folder!
The parameter is: DONOTCREATEDESKTOPSHORTCUT=TRUE
Which means an install string could look like this:
MSIEXEC /I MicrosoftEdgeEnterpriseX64.msi REBOOT=ReallySuppress /qn DONOTCREATEDESKTOPSHORTCUT=TRUE
UPDATE – 22-09-2020 (September 22nd 2020): As of v84.x stable build it is now possible to prevent the pinned Edge shortcut creation during the first launch of Edge. Like the desktop shortcut, this i achieved via a install parameter.
The parameter is: DONOTCREATETASKBARSHORTCUT=TRUE
Which means in install string could look like this:
MSIEXEC /I MicrosoftEdgeEnterpriseX64.msi REBOOT=ReallySuppress /qn DONOTCREATEDESKTOPSHORTCUT=TRUE DONOTCREATETASKBARSHORTCUT=TRUE
The last thing we need to do, is to disable the services and delete the scheduled tasks that are responsible for doing automatic updates of the Edge browser. As with any other application in a non-persistent setup, we will have to disable any auto-update feature.
Here is a small post-install PowerShell script which will do the shortcut cleanup and disable the services and delete the scheduled tasks responsible for the auto-update feature in Edge:
UPDATE – 21-04-2020 (april 21 2020): I have removed the edgeupdatem service from the script below, as it triggered an error in Edge and an accompanied UAC prompt, when automatic update is disabled via GPO. The master_preferences file copy is also removed.
If you have en earlier version of the script, please update it with the new information.
The update error received, when the edgeupdatem service is disabled:
UPDATE – 28-05-2020 (may 28 2020): I have added Remove-Item -Path “HKLM:SOFTWAREMicrosoftActive SetupInstalled Components{9459C573-B17A-45AE-9F64-1857B5D58CEE}” -Force to the install script. This prevents a pinned Edge shortcut in the taskbar from being created. There are other solutions to this issue, which I have described in this article.
Now with the Edge browser installed we can move on to some basic configuration of the browser.
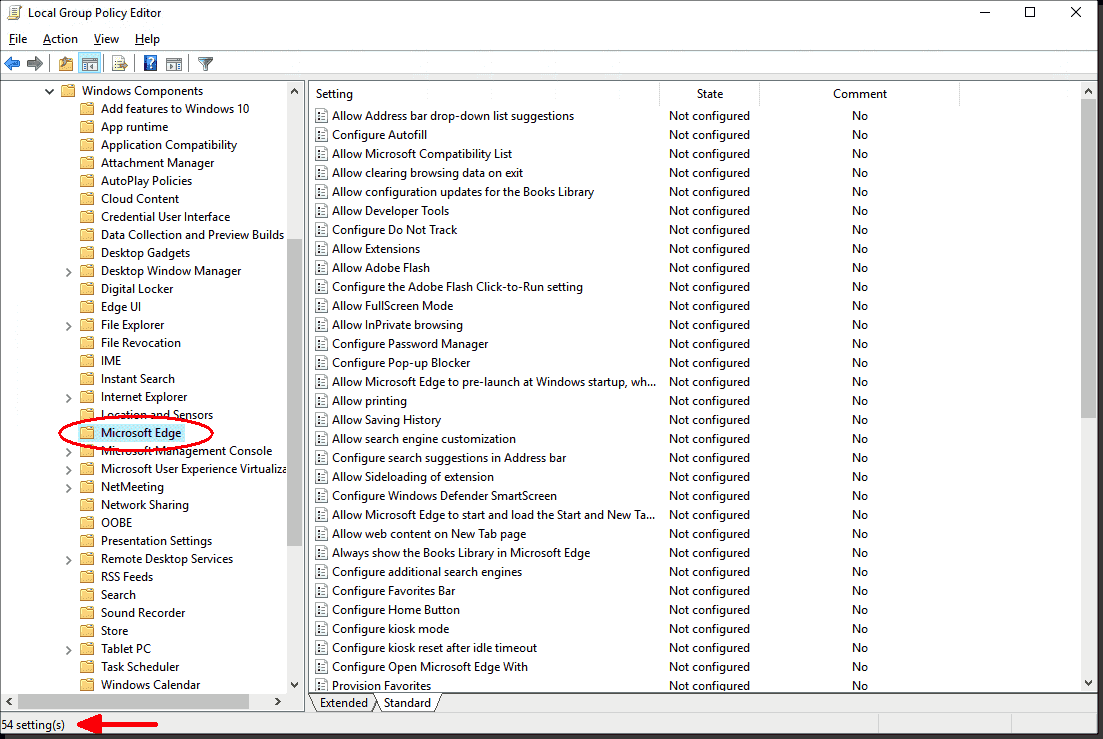
Group Policy Configuration
As mentioned earlier Microsoft has a baseline security GPO, and I would recommend to import this in your current environment, obviously you will have to do some testing, but from what I have seen, the current settings shouldn’t be “destructive” meaning, that nothing is broken in the browser. I will bring one additional group policy settings to the table, which are not found in the security baseline GPO. Any additional configurations should be added to another (new) GPO which should be linked to the same OU as the baseline GPO, but with a higher link order.
So in short, you end out with two GPOs. One GPO with the Microsoft security baseline settings, and one with any additional settings you configure.
App store website. Here is what a GPO configuration and link order could look like:
Microsoft Edge Remote Desktop Access

If you are unfamiliar with importing GPO settings, I would recommend looking at this guide: Mac app store games.
The benefit of doing it this way, is that when Microsoft eventually release updates to their security baseline GPO, your can safely import these updated settings to the baseline GPO or a new GPO, and still have your own custom settings apply, as they are in another GPO.
The Microsoft Edge v79.x Security Baseline GPO contains the security baseline settings from Microsoft, and as mentioned this GPO shouldn’t be modified, as it will complicate any future updates of the GPO settings.
The Microsoft Edge v79.x Additional Configuration GPO should contain whatever policy configurations that applies to your setup. In here I have configured the “Update policy override” the reason for this is that if the user manually triggers the update of Edge, the user is prompted by UAC asking for an administrative username and password, not good,
Microsoft Edge Remote Desktop App
This concludes the guide and you are ready to start testing the Microsoft Edge browser in your Citrix environment and eventually releasing it to production.